Differences Between Asexual and Sexual Reproduction: Reproduction is the process of genetic material being passed down from one generation to the next. As a result, new members of a species or creatures are born. Furthermore, organisms reproduce to perpetuate races. As a result, this aids in their population growth and survival on this planet.
Humans, animals, plants, algae, fungi, and other microbes, for example, reproduce as a natural rule, a way of guaranteeing the species’ existence, and in the framework of evolution. Sexual and asexual reproduction are the two major categories of reproduction. Each has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Vertebrates, such as humans, rely solely on sexual reproduction to reproduce. Asexual reproduction is used by many lower creatures, such as amoeba.
Let’s examine the distinction between sexual and asexual reproduction.
Recommended: Notable scientists in history and their inventions
Definition Of Sexual Reproduction
The term “sexual reproduction” refers to a type of reproduction in which one or more organisms or individuals are involved. The gametes then unite and produce progeny. In addition, the children have distinct personalities. Sexual organs can be found in both male and female species. As a result, when male and female organisms reproduce, their sexual organs come into touch.
Recommended: Differences between plant and animal cells
Types Of Sexual Reproduction
1. Bacteria and Archaea Sexual Reproduction: Asexual reproduction is the most common mode of reproduction for prokaryotes. However, sexual reproduction techniques include lateral gene transfer, which occurs during conjugation, transformation, and transduction.
2. Fungi Sexual Reproduction: Resting spores are produced by sexual reproduction in fungus. These spores are employed to help organisms survive in hostile environments. In the sexual reproduction of fungus, there are three phases: plasmogamy, karyogamy, and meiosis.
The cytoplasm of the two-parent cells is united during plasmogamy. During karyogamy, the two nuclei of the united cells are merged. Finally, haploid gametes are created during meiosis, which is then formed into spores.
Also see: Characteristics of a good scientist
3. Reproduction In Plant: These plants’ life cycle begins with a haploid spore that develops into the dominant form of the life cycle. The gametophyte, which is a photosynthesizing multicellular creature with leaf-like features, is the haploid dominant. Antheridia make up this multicellular organism, which produces haploid gametes by mitosis.
A diploid zygote is produced when gametes are fertilized. The sporophyte is produced when the zygote divides by mitotic division. In the sporophyte, spore capsules are formed. Meiosis is the process through which they create spores.
Gametophytes, which generate sperm and eggs, are formed when spores germinate. To fertilize the egg, sperm must swim through a thin film of water. The zygote that is produced develops into a new sporophyte. Flowering plants’ reproductive organs are their flowers. The anther produces pollen grains, which contain the male gametophyte. The ovary houses the female gametophyte. The fertilized zygote grows into a fruit with seeds.
4. Reproduction in Animals: Male insects generate spermatozoa, whereas female insects create ova. The zygote is created through fertilization. To create gametes, fertilize the gametes, and develop the zygote into a new birth, higher animals, such as mammals, have complicated reproductive organs.
Definition Of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction occurs when just one organism reproduces. As a result, the gametes do not fuse during the procedure. As a result, the children will look exactly like their parents. You’ll also see that asexual reproduction can take several forms. Binary fission, for example, occurs when cells divide in half and produce a clone of the parent. We also have a budding, fragmentation, parthenogenesis, and other processes.
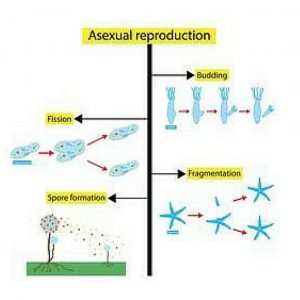
Also see: Advantages and Disadvantages of Being a Teacher
Types Of Asexual Reproduction
1. Fission: There are two types of fission: binary fission and multiple fission. In binary fission, the parent organism is replaced by two daughter organisms. Binary fission is typically seen in bacteria and archaea. In protists, multiple fission occurs. To form many daughter cells, the nucleus is divided several times.
2. Budding: Some fungi, such as baker’s yeast, generate protrusions that allow the mother cell to form a daughter cell. Hydra also reproduces asexually by budding. As a child grows into an adult, the daughter organism separates from the mother organism.
Also see: Best science courses to study in the university
3. Vegetation Propagation: Plants reproduce asexually without producing seeds or spores during vegetative propagation. Vegetative propagation includes the production of plantlets on Kalanchoe leaves, the formation of new plants from rhizomes or stolons in strawberries, and the formation of bulbs in tulips or tubers in dahlia.
4. Sporogenesis: Sporogenesis is the process of the formation of spores. During asexual reproduction, plants and algae create spores by a process known as sporadic meiosis. By mitosis, the spores generate haploid gametophytes, which produce gametes. The zygote is formed when gametes are fertilized, and the sporophyte is formed when the zygote is fertilized.

Also see: Tips to become good in Physics
Characteristics Of Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is mostly used by single-celled organisms, as previously stated. It is considerably easier and needs less energy to replicate this manner because they are only one cell in size. The nuclear envelope disintegrates during mitosis, DNA is duplicated, and a new nuclear envelope is formed, with each set of DNA now separated. The cell pinches in half, resulting in two cells belonging to the same organism. Asexual reproduction is used by bacteria, yeast, and archaebacteria.
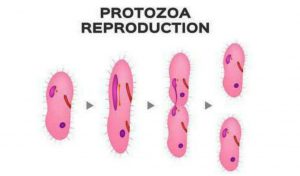
When the conditions are correct, even plants and animals use this approach to pass on their genes. Through the exchange of plasmids, bacteria can share sections of their DNA (small organelles). This allows for the sharing of modest amounts of DNA, but not to the point of sexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction has various advantages. Because only one organism is required to produce more, if everything else has been killed off, one organism can quickly replenish the population. Asexual reproduction necessitates fewer resources and time. Some water animals, such as sponges, can reproduce by budding. The creature’s small pit pinches off, floats away, and grows into a full-sized organism. If resources become scarce or predators become too plentiful, this may occur. Some plants do not require pollination to bear fruit. Without fertilizer, citrus trees can produce fruit with seeds.
Recommended: Advantages and Disadvantages of friction
Characteristics Of Sexual Reproduction
Complex creatures are more likely to employ sexual reproduction. Sea sponges and bacteria are simple species, whereas lions, tigers, and bears are more complex. They have complex organ systems with numerous cell and tissue types. Sexual reproduction allows for the interchange and recombination of genetic material, resulting in a population that is diverse and diversified enough to tolerate a wide range of diseases. It also permits a species to differentiate to better adapt to its surroundings. Mitosis-induced mutations can be passed on to progeny. Many mutations are eliminated before they reach progeny in sexual reproduction and meiosis. The issue of sex, or gender, arises in sexual reproduction.
Male and female are found in both plants and animals, some in the same individual and others in distinct ones. Hermaphrodites are organisms that are both male and female. The genetic information is the same in hermaphroditic organism reproduction, but it is put together in different ways.
There are several methods for sexual reproduction. In any case, two sex cells from different people combine to make a zygote, which is a single cell that will multiply to form an individual. Fertilization occurs when two cells exchange genetic information and the zygote is formed. Fertilization can occur either internally, as in humans, or externally, as in frogs and fish, as well as flowering plants.
Recommended: Characteristics of Scientific Knowledge
Differences Between the Sexual And Asexual Reproduction
1. Sexual Reproduction: Almost all animals, plants, and other life forms, including fungi, bacteria, and protists, have sexual reproduction. Lower animals and plants, as well as fungi, protozoans, and bacteria, all have asexual reproduction.
2. Energy involved: Sexual reproduction necessitates a large amount of energy since a partner must be located, and in some animals, an elaborate wooing is required, which is energy-intensive. Because there is no need for a mate, asexual reproduction consumes extremely little energy. The cell simply divides.
Also see: Countries with the best justice system in the world
3. Type Of Cell Division: The cell division that occurs during sexual reproduction is known as meiosis. It results in the formation of four haploid cells from a diploid cell that has dived twice. In asexual reproduction, mitosis is the process of cell division. One diploid cell divides once, resulting in the formation of two diploid cells.
4. Time Involved: Because a partner must be found and the cell must divide twice during sexual reproduction, it takes a long time. Because there is no need for a mate and the cell only divides once, asexual reproduction takes little time.
5. Genetic Diversity:
Sexual Reproduction: Chromosomal crossing over allows for genetic recombination, resulting in children with genetic variants.
Asexual Reproduction: Because mitosis is used during cell division, daughter cells are genetically identical to their parents.
Also see: Art and Science, Which is more important? Answered
6. Evolutionary Contribution:
Sexual Reproduction: During sexual reproduction, genetic variety among children permits evolution to continue.
Asexual Reproduction: Asexual reproduction allows for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
7. Gamete Formation: Male and female gametes are produced during sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction does not result in the formation of gametes.
8. Units of reproduction: During sexual reproduction, germ cells serve as reproductive units. In asexual reproduction, somatic cells serve as reproductive units.
Also see: Most profitable skills to learn in 2022
9. Fertilizer: In sexual reproduction, To obtain the zygote, male and female gametes are fertilized. Asexual reproduction does not result in fertilization.
10. Number of Parents: Sexual reproduction is a bi-parental process. Asexual reproduction is a process in which only one parent is involved.
11. Progeny: Sexual reproduction progeny are very healthy. Asexual Reproduction: Asexual reproduction produces healthy or slightly healthy offspring.
Also see: Differences between Java and JavaScript
12. Lifespan: Sexual reproduction cells have a limited lifespan. Asexual Reproduction: Asexually reproduced cells are thought to be immortal.
13. Reproductive Organs: Sexual reproduction necessitates the presence of prominent male and female reproductive organs. Asexual reproduction does not necessitate the use of reproductive organs.
Recommended: Causes, Effects and Solutions to Brain drain in Africa
Conclusion
Cell division and the transfer of genetic information into new cells are involved in both sexual and asexual reproduction. Both kinds of reproduction can result in new organisms that can reproduce themselves. During meiosis and fertilization, a lot of genetic variation is introduced into sexual reproduction. Depending on whether a mutation occurs during mitosis, asexual reproduction has little or no genetic variation. Both asexual and sexual reproduction have advantages and downsides.

Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka, ACMC, is a lawyer and a certified mediator/conciliator in Nigeria. He is also a developer with knowledge in various programming languages. Samuel is determined to leverage his skills in technology, SEO, and legal practice to revolutionize the legal profession worldwide by creating web and mobile applications that simplify legal research. Sam is also passionate about educating and providing valuable information to people.