Differences Between Osmosis and Diffusion: Biological membranes are known to act as a physical barrier between a live organism’s internal environment and the outside world. While they must be impermeable at some points to prevent some chemicals from entering, they must also be permeable to certain vital substances and nutrients in order for them to enter and exit the cell.
In this article, we’ll look at two forms of biological membrane transport processes that, at first view, appear to be nearly interchangeable: diffusion and osmosis. We’ll also go over the fundamental differences between diffusion and osmosis.
Recommended: Advantages and Disadvantages of being a Doctor
Description of Diffusion and Osmosis
Nutrients, wastes, gases, salts, and other things are all contained in a water solution that surrounds cells. This is a cell’s exterior environment. The plasma membrane’s outer surface interacts with the external world, while the inner surface interacts with the cytoplasm. The plasma membrane thereby regulates what enters and exits the cell.
Some materials can flow through the membrane, but not all. It is stated that the cell membrane is selectively permeable. Small molecules, for instance, could be able to travel across the membrane. The technique is known as passive transport when no energy is required for substances to flow across the membrane. In this post, we’ll look at two types of passive transport: diffusion and osmosis.
Also see: Best Science Courses to study in the University
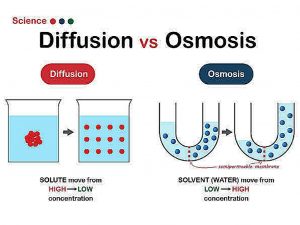
Diffusion
Even if you don’t understand what diffusion is, you’ve probably witnessed it. Can you recall entering into your front door and smelling something delicious emanating from the kitchen? The scents were detected due to the diffusion of molecules from the kitchen to the front entrance of the house.
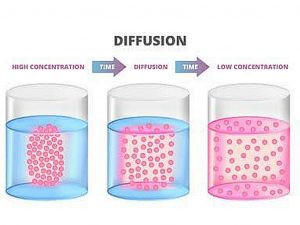
The net flow of molecules from a high-concentration area to a low-concentration area is referred to as diffusion. Because of their kinetic energy, molecules in a gas, liquid, or solid are always moving. Molecules are always moving and colliding with one another. The molecules travel in random directions as a result of these collisions.
More molecules, on the other hand, will be driven towards the less concentrated area over time. As a result, molecular migration is always from more densely packed parts to less densely packed ones. Many things have the ability to disperse. Odors travel via the air, salt travels through water, and nutrients travel from the bloodstream to the tissues of the body.
Diffusion is the random dispersion of particles from a high-concentration area to a low-concentration area. A concentration gradient is the term for this uneven distribution of molecules. Dynamic equilibrium is reached when the molecules are evenly dispersed. Because molecules continue to migrate, the equilibrium is considered to be dynamic, yet there is no net change in concentration over time. The process of diffusion affects both living and nonliving systems. Diffusion is essential for the passage of a vast variety of substances into and out of cells in biological systems, including gases and tiny uncharged molecules.
Recommended: Arts vs Science, Which is Better? Answered
Osmosis
Osmosis is a form of diffusion that details the transfer of water from a increased concentration zone to a low-concentration region over a semi-permeable barrier. Semi-permeable membranes are often very thin layers of material that allow certain items to pass through but restrict others from passing across. Semi-permeable membranes are found in cell membranes. Small biomolecules like oxygen, water, carbon dioxide, and fructose can flow across cell membranes, while bigger molecules like sucrose, proteins, and glycogen cannot.
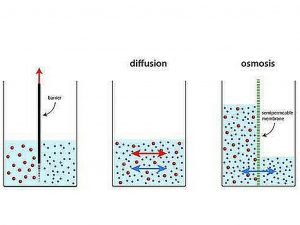
Water molecules would flow from one side with the highest concentration of water to the other with the lowest concentration of water when there is a semi-permeable membrane with more water molecules on one side than the other. This would continue until the water concentrations on both sides of the membrane were equal, establishing dynamic equilibrium.
Recommended: Duties and responsibilities of Children in the Family
More Information on Osmosis
Let’s go at the intricacies of osmosis and diffusion to better grasp the differences between the two. Osmosis is a chemical solution separation technique that involves two components: a solvent and a solute. In addition, when a solute dissolves in a solvent, the final product is a solution.
Due to osmosis, there are three main types of solutions that effect cells. Furthermore, the first type of solution is an isotonic solution, which has the same solute concentration within and outside the cell.
Furthermore, in a hypotonic solution, the concentration of solutes inside the cell is larger than the concentration outside. Finally, there is more solute outside the cell than inside it in a hypertonic solution. Because plant and animal cells can tolerate differing quantities of water, osmosis impacts them differently. In a hypotonic solution, for example, an animal cell will fill with too much water and lyse, or burst open. Plant cells, on the other hand, have a higher water need than animal cells, and their thick cell walls prevent them from bursting.
Also see: Highest Paying Programming Jobs 2022
More Information on Diffusion
Diffusion is characterized by the movement of molecules along a concentration gradient. Furthermore, high-energy molecules like as adenosine triphosphate are not directly involved in this movement (ATP). Diffusion and reverse osmosis are not interchangeable terms. Diffusion also involves the flow of molecules from a location of greater concentration to a region of lower concentration.
Reverse osmosis, on the other hand, occurs when water moves over the membrane in the opposite direction of the concentration gradient, from lower to higher concentration.
There’s also a distinction to be made between diffusion and active transportation. This is because active transport is defined as the transportation of molecules and ions against a gradient concentration while exerting energy expenditure. Diffusion, on the other hand, requires no energy cost.
Recommended: Difference Between Civil Engineering and Architecture
Differences between osmosis and diffusion
1. Definition
Osmosis: The process of moving solvent molecules across a semi-permeable membrane to an area with a greater solute concentration is known as osmosis.
Diffusion: In any form of combination, diffusion is the movement of molecules along a concentration gradient.
2. Solute and solvent movement
Osmosis: Only the solvent (water molecules) moves in osmosis.
Diffusion: Both the solute and the solvent molecules move during diffusion.
3. Semi-permeable membrane
Osmosis: The semi-permeable membrane is engaged in osmosis.
Diffusion: The semi-permeable membrane is not engaged in diffusion.
Recommended: Most Talented People In The World 2022 (With Pictures): Top 10
4. Dependence
Osmosis: It is determined by the solute potential. In addition, it is mostly determined by the amount of solute particles in the solvent.
Diffusion: It is unaffected by solute, water, or pressure potentials. In addition, it is mostly dependent on the existence of other particles.
5. Movement
Osmosis: Osmosis moves in such a way that it tries to equalize solvent concentration, but this does not happen.
Diffusion: Diffusion moves the concentration around in the system, balancing it out.
6. Importance
Osmosis: Osmosis is necessary for the distribution of nutrients throughout the cell as well as the elimination of metabolic waste.
Diffusion is necessary for the production of energy through respiration and photosynthesis.
7. Hydrostatic pressure and turgor pressure
Osmosis: Osmosis is opposed by these two forces.
Diffusion: Diffusion is not generally subjected to these two pressures.
8. Mineral and nutrients absorption
Osmosis: Mineral and nutrient absorption are unrelated.
Diffusion: It aids in mineral and vitamin absorption.
9. Reversibility
Osmosis: By providing more pressure to the solution side, the entire process may either be stopped or reversed.
Diffusion: This is a procedure that can’t be halted or undone.
10. Type of solution
Osmosis: It only happens amongst solutions of the same kind.
Diffusion: This occurs between solutions that are similar and those that are distinct.
Recommended: Differences Between Agent And Servant
Conclusion
There are two types of transport mechanisms for incorporating the flow of molecules into and out of the cell: osmosis and diffusion. These two systems are passive transport systems since they do not require any additional energy to operate, while assisted diffusion does. The medium in which the two systems are used is the most significant difference between them. Although osmosis can only work in a liquid media, diffusion may happen in all three: solid, liquid, and gas.
Furthermore, although diffusion does not necessitate a semi-permeable membrane, osmosis must. Osmosis is demonstrated by the uptake of water by plants. When a drop of food coloring is dropped into a glass of water, diffusion occurs, and the entire water content gets colored.

Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka, ACMC, is a lawyer and a certified mediator/conciliator in Nigeria. He is also a developer with knowledge in various programming languages. Samuel is determined to leverage his skills in technology, SEO, and legal practice to revolutionize the legal profession worldwide by creating web and mobile applications that simplify legal research. Sam is also passionate about educating and providing valuable information to people.